Cello Sheet Music
 "There are two means of refuge from the miseries of life: music and cats." Albert Schweitzer
"There are two means of refuge from the miseries of life: music and cats." Albert Schweitzer
John Williams

John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932) is an American composer, conductor, and pianist. In a career that spans six decades, Williams has composed many of the most famous film scores in Hollywood history, including Star Wars, Superman, Home Alone, the first three Harry Potter movies and all but two of Steven Spielberg's feature films including the Indiana Jones series, Schindler's List, E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial, Jurassic Park and Jaws. He also composed the soundtrack for the hit 1960s television series Lost in Space as well as the fanfare of the DreamWorks Pictures' logo.
Williams has composed theme music for four Olympic Games, the NBC Nightly News, the rededication of the Statue of Liberty, and numerous television series and concert pieces. He served as the principal conductor of the Boston Pops Orchestra from 1980 to 1993, and is now the orchestra's laureate conductor.
Williams is a five-time winner of the Academy Award. He has also won four Golden Globe Awards, seven BAFTA Awards and 21 Grammy Awards. With 45 Academy Award nominations, Williams is, together with composer Alfred Newman, the second most nominated person after Walt Disney. He was inducted into the Hollywood Bowl Hall of Fame in 2000, and was a recipient of the Kennedy Center Honors in 2004.
Williams has composed theme music for four Olympic Games, the NBC Nightly News, the rededication of the Statue of Liberty, and numerous television series and concert pieces. He served as the principal conductor of the Boston Pops Orchestra from 1980 to 1993, and is now the orchestra's laureate conductor.
Williams is a five-time winner of the Academy Award. He has also won four Golden Globe Awards, seven BAFTA Awards and 21 Grammy Awards. With 45 Academy Award nominations, Williams is, together with composer Alfred Newman, the second most nominated person after Walt Disney. He was inducted into the Hollywood Bowl Hall of Fame in 2000, and was a recipient of the Kennedy Center Honors in 2004.
Vivaldi

Antonio Lucio Vivaldi (March 4, 1678 â July 28, 1741), nicknamed il Prete Rosso ("The Red Priest"), was a Venetian priest and Baroque music composer, as well as a famous virtuoso violinist; he was born and raised in the Republic of Venice. The Four Seasons, a series of four violin concerti, is his best-known work and a highly popular Baroque piece.
Many of Vivaldi's compositions reflect a flamboyant, almost playful, exuberance. Most of Vivaldi's repertoire was rediscovered only in the first half of the 20th century in Turin and Genoa and was published in the second half. Vivaldi's music is innovative, breaking a consolidated tradition in schemes; he gave brightness to the formal and the rhythmic structure of the concerto, repeatedly looking for harmonic contrasts and innovative melodies and themes. Moreover, Vivaldi was able to compose nonacademic music, particularly meant to be appreciated by the wide public and not only by an intellectual minority. The joyful appearance of his music reveals in this regard a transmissible joy of composing; these are among the causes of the vast popularity of his music. This popularity soon made him famous in other countries such as France which was, at the time, very independent concerning its musical taste.
Vivaldi is considered one of the composers who brought Baroque music (with its typical contrast among heavy sonorities) to evolve into a classical style. Johann Sebastian Bach was deeply influenced by Vivaldi's concertos and arias (recalled in his Johannes Passion, Matthäuspassion, and cantatas). Bach transcribed a number of Vivaldi's concerti for solo keyboard, along with a number for orchestra, including the famous Concerto for Four Violins and Violoncello, Strings and Continuo (RV 580).
Many of Vivaldi's compositions reflect a flamboyant, almost playful, exuberance. Most of Vivaldi's repertoire was rediscovered only in the first half of the 20th century in Turin and Genoa and was published in the second half. Vivaldi's music is innovative, breaking a consolidated tradition in schemes; he gave brightness to the formal and the rhythmic structure of the concerto, repeatedly looking for harmonic contrasts and innovative melodies and themes. Moreover, Vivaldi was able to compose nonacademic music, particularly meant to be appreciated by the wide public and not only by an intellectual minority. The joyful appearance of his music reveals in this regard a transmissible joy of composing; these are among the causes of the vast popularity of his music. This popularity soon made him famous in other countries such as France which was, at the time, very independent concerning its musical taste.
Vivaldi is considered one of the composers who brought Baroque music (with its typical contrast among heavy sonorities) to evolve into a classical style. Johann Sebastian Bach was deeply influenced by Vivaldi's concertos and arias (recalled in his Johannes Passion, Matthäuspassion, and cantatas). Bach transcribed a number of Vivaldi's concerti for solo keyboard, along with a number for orchestra, including the famous Concerto for Four Violins and Violoncello, Strings and Continuo (RV 580).
Schubert

Franz Peter Schubert (January 31, 1797 – November 19, 1828) was an Austrian composer. He wrote some 600 lieder, nine symphonies (including the famous "Unfinished Symphony"), liturgical music, operas, and a large body of chamber and solo piano music. He is particularly noted for his original melodic and harmonic writing.
While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (including his teacher Antonio Salieri, and the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wider appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
While he was clearly influenced by the Classical sonata forms of Beethoven and Mozart (his early works, among them notably the 5th Symphony, are particularly Mozartean), his formal structures and his developments tend to give the impression more of melodic development than of harmonic drama. This combination of Classical form and long-breathed Romantic melody sometimes lends them a discursive style: his 9th Symphony was described by Robert Schumann as running to "heavenly lengths". His harmonic innovations include movements in which the first section ends in the key of the subdominant rather than the dominant (as in the last movement of the Trout Quintet). Schubert's practice here was a forerunner of the common Romantic technique of relaxing, rather than raising, tension in the middle of a movement, with final resolution postponed to the very end.
While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (including his teacher Antonio Salieri, and the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wider appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
While he was clearly influenced by the Classical sonata forms of Beethoven and Mozart (his early works, among them notably the 5th Symphony, are particularly Mozartean), his formal structures and his developments tend to give the impression more of melodic development than of harmonic drama. This combination of Classical form and long-breathed Romantic melody sometimes lends them a discursive style: his 9th Symphony was described by Robert Schumann as running to "heavenly lengths". His harmonic innovations include movements in which the first section ends in the key of the subdominant rather than the dominant (as in the last movement of the Trout Quintet). Schubert's practice here was a forerunner of the common Romantic technique of relaxing, rather than raising, tension in the middle of a movement, with final resolution postponed to the very end.
Haydn

Franz Joseph Haydn (March 31, 1732 – May 31, 1809) was one of the most prominent composers of the classical period, and is called by some the "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String Quartet".
A life-long resident of Austria, Haydn spent most of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Hungarian Esterházy family on their remote estate. Isolated from other composers and trends in music until the later part of his long life, he was, as he put it, "forced to become original".
Although Haydn is still often called "Franz Joseph Haydn", the composer did not use the name "Franz" during his lifetime and this misnomer is avoided by modern scholars and historians. Joseph Haydn was the brother of Michael Haydn, himself a highly regarded composer, and Johann Evangelist Haydn, a tenor.
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly.
Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Mozart and Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called "monothematic exposition", in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development.
Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous false endings (e.g., in the quartets Op. 33 No. 2 and Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of Op. 50 No. 1.
A life-long resident of Austria, Haydn spent most of his career as a court musician for the wealthy Hungarian Esterházy family on their remote estate. Isolated from other composers and trends in music until the later part of his long life, he was, as he put it, "forced to become original".
Although Haydn is still often called "Franz Joseph Haydn", the composer did not use the name "Franz" during his lifetime and this misnomer is avoided by modern scholars and historians. Joseph Haydn was the brother of Michael Haydn, himself a highly regarded composer, and Johann Evangelist Haydn, a tenor.
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly.
Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Mozart and Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called "monothematic exposition", in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development.
Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous false endings (e.g., in the quartets Op. 33 No. 2 and Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of Op. 50 No. 1.
Apocalyptica

Apocalyptica is a Finnish cello metal band, composed of classically trained cellists and, since 2005, a drummer. Three of the cellists are graduates of the Sibelius Academy in Helsinki, Finland. Their music features elements from classical music, neo-classical metal, thrash metal, and symphonic metal.
Mozart

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, full name Johann Chrysostom Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical era. His over 600 compositions include works widely acknowledged as pinnacles of symphonic, concertante, chamber, piano, operatic, and choral music. Mozart is among the most enduringly popular of classical composers, and many of his works are part of the standard concert repertoire.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
Mozart's music, like Haydn's, stands as an archetypal example of the Classical style. His works spanned the period during which that style transformed from one exemplified by the style galant to one that began to incorporate some of the contrapuntal complexities of the late Baroque, complexities against which the galant style had been a reaction. Mozart's own stylistic development closely paralleled the development of the classical style as a whole. In addition, he was a versatile composer and wrote in almost every major genre, including symphony, opera, the solo concerto, chamber music including string quartet and string quintet, and the piano sonata. While none of these genres were new, the piano concerto was almost single-handedly developed and popularized by Mozart. He also wrote a great deal of religious music, including masses; and he composed many dances, divertimenti, serenades, and other forms of light entertainment.
The central traits of the classical style can be identified in Mozart's music. Clarity, balance, and transparency are hallmarks of his work.
J. S. Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (21 March 1685, O.S.31 March 1685, N.S. – 28 July 1750, N.S.) was a German composer, organist, harpsichordist, violist, and violinist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he did not introduce new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation, and the adaptation of rhythms, forms and textures from abroad, particularly from Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth, technical command and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Goldberg Variations, the Partitas, The Well-Tempered Clavier, the Mass in B minor, the St Matthew Passion, the St John Passion, the Magnificat, A Musical Offering, The Art of Fugue, the English and French Suites, the Sonatas and Partitas for solo violin, the Cello Suites, more than 200 surviving cantatas, and a similar number of organ works, including the famous Toccata and Fugue in D minor and Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, as well as the Great Eighteen Chorale Preludes and Organ Mass.
Bach's abilities as an organist were highly respected throughout Europe during his lifetime, although he was not widely recognised as a great composer until a revival of interest and performances of his music in the first half of the 19th century. He is now generally regarded as one of the main composers of the Baroque style, and as one of the greatest composers of all time.
Revered for their intellectual depth, technical command and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Goldberg Variations, the Partitas, The Well-Tempered Clavier, the Mass in B minor, the St Matthew Passion, the St John Passion, the Magnificat, A Musical Offering, The Art of Fugue, the English and French Suites, the Sonatas and Partitas for solo violin, the Cello Suites, more than 200 surviving cantatas, and a similar number of organ works, including the famous Toccata and Fugue in D minor and Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, as well as the Great Eighteen Chorale Preludes and Organ Mass.
Bach's abilities as an organist were highly respected throughout Europe during his lifetime, although he was not widely recognised as a great composer until a revival of interest and performances of his music in the first half of the 19th century. He is now generally regarded as one of the main composers of the Baroque style, and as one of the greatest composers of all time.
Bach

Johann Sebastian Bach (31 March 1685 – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and organist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he introduced no new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation in composition for diverse musical forces, and the adaptation of rhythms and textures from abroad, particularly Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Revered for their intellectual depth and technical and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg concertos; the Goldberg Variations; the English Suites, French Suites, Partitas, and Well-Tempered Clavier; the Mass in B Minor; the St. Matthew Passion; the St. John Passion; The Musical Offering; The Art of Fugue; the Sonatas and Partitas for violin solo; the Cello Suites; more than 200 surviving cantatas; and a similar number of organ works, including the celebrated Toccata and Fugue in D Minor.
While Bach's fame as an organist was great during his lifetime, he was not particularly well-known as a composer. His adherence to Baroque forms and contrapuntal style was considered "old-fashioned" by his contemporaries, especially late in his career when the musical fashion tended towards Rococo and later Classical styles. A revival of interest and performances of his music began early in the 19th century, and he is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Beethoven

Ludwig van Beethoven (16 December 1770 - 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most respected and influential composers of all time.
Born in Bonn, then in the Electorate of Cologne (now in modern-day Germany), he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. Beethoven's hearing gradually deteriorated beginning in his twenties, yet he continued to compose masterpieces, and to conduct and perform, even after he was completely deaf.
Born in Bonn, then in the Electorate of Cologne (now in modern-day Germany), he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. Beethoven's hearing gradually deteriorated beginning in his twenties, yet he continued to compose masterpieces, and to conduct and perform, even after he was completely deaf.
Grieg

Edvard Hagerup Grieg (/ɡriːɡ/ GREEG, Norwegian: ; 15 June 1843 – 4 September 1907) was a Norwegian composer and pianist. He is widely considered one of the leading Romantic era composers, and his music is part of the standard classical repertoire worldwide. His use and development of Norwegian folk music in his own compositions brought the music of Norway to international consciousness, as well as helping to develop a national identity, much as Jean Sibelius and Bedřich Smetana did in Finland and Bohemia, respectively.
Grieg is the most celebrated person from the city of Bergen, with numerous statues depicting his image, and many cultural entities named after him: the city's largest concert building (Grieg Hall), its most advanced music school (Grieg Academy) and its professional choir (Edvard Grieg Kor). The Edvard Grieg Museum at Grieg's former home, Troldhaugen, is dedicated to his legacy.
Grieg is the most celebrated person from the city of Bergen, with numerous statues depicting his image, and many cultural entities named after him: the city's largest concert building (Grieg Hall), its most advanced music school (Grieg Academy) and its professional choir (Edvard Grieg Kor). The Edvard Grieg Museum at Grieg's former home, Troldhaugen, is dedicated to his legacy.
The Beatles

The Beatles were a pop and rock group from Liverpool, England formed in 1960. Primarily consisting of John Lennon (rhythm guitar, vocals), Paul McCartney (bass guitar, vocals), George Harrison (lead guitar, vocals) and Ringo Starr (drums, vocals) throughout their career, The Beatles are recognised for leading the mid-1960s musical "British Invasion" into the United States. Although their initial musical style was rooted in 1950s rock and roll and homegrown skiffle, the group explored genres ranging from Tin Pan Alley to psychedelic rock. Their clothes, styles, and statements made them trend-setters, while their growing social awareness saw their influence extend into the social and cultural revolutions of the 1960s. After the band broke up in 1970, all four members embarked upon solo careers.
The Beatles are one of the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed bands in the history of popular music, selling over a billion records internationally. In the United Kingdom, The Beatles released more than 40 different singles, albums, and EPs that reached number one, earning more number one albums (15) than any other group in UK chart history. This commercial success was repeated in many other countries; their record company, EMI, estimated that by 1985 they had sold over one billion records worldwide. According to the Recording Industry Association of America, The Beatles have sold more albums in the United States than any other band. In 2004, Rolling Stone magazine ranked The Beatles number one on its list of 100 Greatest Artists of All Time. According to that same magazine, The Beatles' innovative music and cultural impact helped define the 1960s, and their influence on pop culture is still evident today. In 2008, Billboard magazine released a list of top-selling Hot 100 artists to celebrate the chart's fiftieth anniversary; The Beatles reached #1 again.
The Beatles are one of the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed bands in the history of popular music, selling over a billion records internationally. In the United Kingdom, The Beatles released more than 40 different singles, albums, and EPs that reached number one, earning more number one albums (15) than any other group in UK chart history. This commercial success was repeated in many other countries; their record company, EMI, estimated that by 1985 they had sold over one billion records worldwide. According to the Recording Industry Association of America, The Beatles have sold more albums in the United States than any other band. In 2004, Rolling Stone magazine ranked The Beatles number one on its list of 100 Greatest Artists of All Time. According to that same magazine, The Beatles' innovative music and cultural impact helped define the 1960s, and their influence on pop culture is still evident today. In 2008, Billboard magazine released a list of top-selling Hot 100 artists to celebrate the chart's fiftieth anniversary; The Beatles reached #1 again.
Bernard Herrmann

Bernard Herrmann (June 29, 1911 – December 24, 1975) was an American composer noted for his work in motion pictures.
An Academy Award-winner (for The Devil and Daniel Webster, 1941), Herrmann is particularly known for his collaborations with director Alfred Hitchcock, most famously Psycho, North by Northwest, The Man Who Knew Too Much, and Vertigo. He also composed notable scores for many other movies, including Citizen Kane, The Ghost and Mrs. Muir, Cape Fear, and Taxi Driver. He worked extensively in radio drama (most notably for Orson Welles), composed the scores for several fantasy films by Ray Harryhausen, and many TV programs including most notably Rod Serling's The Twilight Zone.
An Academy Award-winner (for The Devil and Daniel Webster, 1941), Herrmann is particularly known for his collaborations with director Alfred Hitchcock, most famously Psycho, North by Northwest, The Man Who Knew Too Much, and Vertigo. He also composed notable scores for many other movies, including Citizen Kane, The Ghost and Mrs. Muir, Cape Fear, and Taxi Driver. He worked extensively in radio drama (most notably for Orson Welles), composed the scores for several fantasy films by Ray Harryhausen, and many TV programs including most notably Rod Serling's The Twilight Zone.
Astor Piazzolla

Ástor Pantaleón Piazzolla (March 11, 1921 – July 4, 1992) was an Argentine tango composer and bandoneón player. His oeuvre revolutionized the traditional tango into a new style termed nuevo tango, incorporating elements from jazz and classical music. An excellent bandoneonist, he regularly performed his own compositions with different ensembles.
Piazzolla's nuevo tango was distinct from the traditional tango in its incorporation of elements of jazz, its use of extended harmonies and dissonance, its use of counterpoint, and its ventures into extended compositional forms. As Argentine psychoanalyst Carlos Kuri has pointed out, Piazzolla's fusion of tango with this wide range of other recognizable Western musical elements was so successful that it produced a new individual style transcending these influences. It is precisely this success, and individuality, that makes it hard to pin down where particular influences reside in his compositions, but some aspects are clear. The use of the passacaglia technique of a circulating bass line and harmonic sequence, invented and much used in 17th and 18th century baroque music but also central to the idea of jazz "changes", predominates in most of Piazzolla's mature compositions. Another clear reference to the baroque is the often complex and virtuosic counterpoint that sometimes follows strict fugal behavior but more often simply allows each performer in the group to assert his voice. A further technique that emphasises this sense of democracy and freedom among the musicians is improvisation that is borrowed from jazz in concept, but in practice involves a different vocabulary of scales and rhythms that stay within the parameters of the established tango sound-world. Pablo Ziegler has been particularly responsible for developing this aspect of the style both within Piazzolla's groups and since the composer's death.
Piazzolla's nuevo tango was distinct from the traditional tango in its incorporation of elements of jazz, its use of extended harmonies and dissonance, its use of counterpoint, and its ventures into extended compositional forms. As Argentine psychoanalyst Carlos Kuri has pointed out, Piazzolla's fusion of tango with this wide range of other recognizable Western musical elements was so successful that it produced a new individual style transcending these influences. It is precisely this success, and individuality, that makes it hard to pin down where particular influences reside in his compositions, but some aspects are clear. The use of the passacaglia technique of a circulating bass line and harmonic sequence, invented and much used in 17th and 18th century baroque music but also central to the idea of jazz "changes", predominates in most of Piazzolla's mature compositions. Another clear reference to the baroque is the often complex and virtuosic counterpoint that sometimes follows strict fugal behavior but more often simply allows each performer in the group to assert his voice. A further technique that emphasises this sense of democracy and freedom among the musicians is improvisation that is borrowed from jazz in concept, but in practice involves a different vocabulary of scales and rhythms that stay within the parameters of the established tango sound-world. Pablo Ziegler has been particularly responsible for developing this aspect of the style both within Piazzolla's groups and since the composer's death.
Franz Schubert

Franz Peter Schubert (German pronunciation: ; January 31, 1797 – November 19, 1828) was an Austrian composer. He wrote some 600 Lieder, nine symphonies (including the famous "Unfinished Symphony"), liturgical music, operas, some incidental music, and a large body of chamber and solo piano music. He is particularly noted for his original melodic and harmonic writing.
Schubert was born into a musical family, and received formal musical training through much of his childhood. While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (amongst them the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wide appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. He made some money from published works, and occasionally gave private musical instruction. In the last year of his life he began to receive wider acclaim. He died at the age of 31 of "typhoid fever", a diagnosis which was vague at the time; several scholars suspect the real illness was tertiary syphilis.
Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death. Composers like Franz Liszt, Robert Schumann and Felix Mendelssohn discovered, collected, and championed his works in the 19th century, as did musicologist Sir George Grove. Franz Schubert is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Schubert was born into a musical family, and received formal musical training through much of his childhood. While Schubert had a close circle of friends and associates who admired his work (amongst them the prominent singer Johann Michael Vogl), wide appreciation of his music during his lifetime was limited at best. He was never able to secure adequate permanent employment, and for most of his career he relied on the support of friends and family. He made some money from published works, and occasionally gave private musical instruction. In the last year of his life he began to receive wider acclaim. He died at the age of 31 of "typhoid fever", a diagnosis which was vague at the time; several scholars suspect the real illness was tertiary syphilis.
Interest in Schubert's work increased dramatically in the decades following his death. Composers like Franz Liszt, Robert Schumann and Felix Mendelssohn discovered, collected, and championed his works in the 19th century, as did musicologist Sir George Grove. Franz Schubert is now widely considered to be one of the greatest composers in the Western tradition.
Scott Joplin

Scott Joplin (between June 1867 and January 1868 – April 1, 1917) was an American musician and composer of ragtime music. He remains the best-known ragtime figure and is regarded as one of the three most important composers of classic ragtime, along with James Scott and Joseph Lamb, and also a precursor to Stride Piano. Decades after his death, his music enjoyed a considerable surge of popularity and critical respect in the 1970s, especially for his most famous composition, "The Entertainer."
Even at the time of publication, Joplin's publisher John Stark was claiming that the rags had obtained classical status, and "lifted ragtime from its low estate and lined it up with Beethoven and Bach".
Even at the time of publication, Joplin's publisher John Stark was claiming that the rags had obtained classical status, and "lifted ragtime from its low estate and lined it up with Beethoven and Bach".
Craig Armstrong

Craig Armstrong OBE (born 1959) is a Scottish composer of modern orchestral music, electronica and film scores.
Armstrong was born in Glasgow, Scotland in 1959. He studied musical composition, violin and piano at the Royal Academy of Music from 1977 to 1981, where he was awarded the Charles Lucas prize and the Harvey Lohr scholarship for composition. He was also awarded the FTCL Fellowship in composition, and won the GLAA Young Jazz Musician of the Year in 1982. Upon completing his studies, Armstrong served as music and dance specialist at the Strathclyde Regional Council in 1984.
Armstrong's score for Baz Luhrmann’s groundbreaking musical Moulin Rouge! earned him AFI’s Composer of the Year, a Golden Globe for Best Original Score of the Year and a BAFTA for Achievement in Film Music. His score for Phillip Noyce’s The Quiet American garnered him the Ivor Novello Award for Best Original Film Score. His other feature film scoring credits include the Oliver Stone drama World Trade Center; the Oscar®-winning bio-pic Ray for which Armstrong was awarded a Grammy for Best Original Score; and the worldwide ensemble comedy smash Love Actually. His scores can also be heard in The Magdalene Sisters, Kiss of the Dragon, The Bone Collector, The Clearing, Plunkett & Macleane, Best Laid Plans, Orphans, Elizabeth: The Golden Age and most recently Louis Leterrier’s Incredible Hulk. His score to William Shakespeare’s Romeo + Juliet (again with Baz Luhrmann) also earned him a BAFTA for Achievement in Film Music and an Ivor Novello.
Armstrong was born in Glasgow, Scotland in 1959. He studied musical composition, violin and piano at the Royal Academy of Music from 1977 to 1981, where he was awarded the Charles Lucas prize and the Harvey Lohr scholarship for composition. He was also awarded the FTCL Fellowship in composition, and won the GLAA Young Jazz Musician of the Year in 1982. Upon completing his studies, Armstrong served as music and dance specialist at the Strathclyde Regional Council in 1984.
Armstrong's score for Baz Luhrmann’s groundbreaking musical Moulin Rouge! earned him AFI’s Composer of the Year, a Golden Globe for Best Original Score of the Year and a BAFTA for Achievement in Film Music. His score for Phillip Noyce’s The Quiet American garnered him the Ivor Novello Award for Best Original Film Score. His other feature film scoring credits include the Oliver Stone drama World Trade Center; the Oscar®-winning bio-pic Ray for which Armstrong was awarded a Grammy for Best Original Score; and the worldwide ensemble comedy smash Love Actually. His scores can also be heard in The Magdalene Sisters, Kiss of the Dragon, The Bone Collector, The Clearing, Plunkett & Macleane, Best Laid Plans, Orphans, Elizabeth: The Golden Age and most recently Louis Leterrier’s Incredible Hulk. His score to William Shakespeare’s Romeo + Juliet (again with Baz Luhrmann) also earned him a BAFTA for Achievement in Film Music and an Ivor Novello.
Alexandre Desplat

Desplat has extensively composed for films, first in France and later in Hollywood, including scores and incidental music for some 100 films among which are Lapse of Memory and Family Express (both 1992), Regarde Les Hommes Tomber (1994), Les Péchés Mortels (1995), the César nominated Un Héros Très Discret (1996), Une Minute De Silence and Sweet Revenge (both 1998), Le Château Des Singes (1999), Home Sweet Home and Reines D'Un Jour (both 2001), the César nominated Sur Mes Lèvres (2002), and Rire Et Châtiment (2003), among others.
Desplat has composed individual songs that have been sung in films by artists such as Akhenaton, Kate Beckinsale, Charlotte Gainsbourg, Valérie Lemercier, Miosotis, and Catherine Ringer. He has also written music for the theatre, including pieces performed at the Comédie Française. Desplat has conducted performances of his music played by the London Symphony Orchestra, the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra, and the Munich Symphony Orchestra. In addition to his composing and performing, Desplat has also given Master Classes at La Sorbonne in Paris and at London's Royal College of Music.
In 2007 he composed the high profile scores for Philip Pullman's The Golden Compass; Zach Helm's directorial debut Mr. Magorium's Wonder Emporium with American composer Aaron Zigman; and the Ang Lee movie Lust, Caution. Prior to these breakout works, he contributed scores for The Luzhin Defence, Girl with a Pearl Earring, Syriana, Birth, Hostage, Casanova, The Nest and The Painted Veil, for which he won the Golden Globe Award for Best Original Score, Los Angeles Film Critics Association Award for Best Music, and the 2006 World Soundtrack Award. He won the 2007 BMI Film Music Award, 2007 World Soundtrack Award, 2007 European Film Award, and received his first Academy Award nomination for Best Original Score for The Queen. He also won the Silver Berlin Bear at the Berlin Film Festival for Best Film Music in The Beat that My Heart Skipped. In 2008, Desplat received his second Oscar nomination for David Fincher's The Curious Case of Benjamin Button.
Desplat's recent projects include Largo Winch, based on the Belgian comic; Afterwards a French-Canadian psychological thriller film directed by Gilles Bourdos in English; Anne Fontaine's Coco avant Chanel based on the life of designer Coco Chanel; Robert Guédiguian's L'Armée du Crime; Cheri, reuniting him with director Stephen Frears, whom he collaborated with on The Queen; Un Prophète reuniting with director Jacques Audiard; Julie & Julia directed by Nora Ephron; Fantastic Mr. Fox, directed by Wes Anderson and based on the novel by Roald Dahl; and New Moon, directed by Chris Weitz, out in November 2009.
Desplat's upcoming projects are The Tree of Life, directed by Terrence Malick, The Ghost, directed by Roman Polanski, and Largo Winch 2 .
Desplat has composed individual songs that have been sung in films by artists such as Akhenaton, Kate Beckinsale, Charlotte Gainsbourg, Valérie Lemercier, Miosotis, and Catherine Ringer. He has also written music for the theatre, including pieces performed at the Comédie Française. Desplat has conducted performances of his music played by the London Symphony Orchestra, the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra, and the Munich Symphony Orchestra. In addition to his composing and performing, Desplat has also given Master Classes at La Sorbonne in Paris and at London's Royal College of Music.
In 2007 he composed the high profile scores for Philip Pullman's The Golden Compass; Zach Helm's directorial debut Mr. Magorium's Wonder Emporium with American composer Aaron Zigman; and the Ang Lee movie Lust, Caution. Prior to these breakout works, he contributed scores for The Luzhin Defence, Girl with a Pearl Earring, Syriana, Birth, Hostage, Casanova, The Nest and The Painted Veil, for which he won the Golden Globe Award for Best Original Score, Los Angeles Film Critics Association Award for Best Music, and the 2006 World Soundtrack Award. He won the 2007 BMI Film Music Award, 2007 World Soundtrack Award, 2007 European Film Award, and received his first Academy Award nomination for Best Original Score for The Queen. He also won the Silver Berlin Bear at the Berlin Film Festival for Best Film Music in The Beat that My Heart Skipped. In 2008, Desplat received his second Oscar nomination for David Fincher's The Curious Case of Benjamin Button.
Desplat's recent projects include Largo Winch, based on the Belgian comic; Afterwards a French-Canadian psychological thriller film directed by Gilles Bourdos in English; Anne Fontaine's Coco avant Chanel based on the life of designer Coco Chanel; Robert Guédiguian's L'Armée du Crime; Cheri, reuniting him with director Stephen Frears, whom he collaborated with on The Queen; Un Prophète reuniting with director Jacques Audiard; Julie & Julia directed by Nora Ephron; Fantastic Mr. Fox, directed by Wes Anderson and based on the novel by Roald Dahl; and New Moon, directed by Chris Weitz, out in November 2009.
Desplat's upcoming projects are The Tree of Life, directed by Terrence Malick, The Ghost, directed by Roman Polanski, and Largo Winch 2 .
Georges Bizet

Georges Bizet (25 October 1838 – 3 June 1875) was a French composer and pianist of the Romantic era. He is best known for the opera Carmen.
Bizet was born at 26 rue de la Tour d'Auvergne in the 9th arrondissement of Paris in 1838. He was registered with the legal name Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, but he was baptised on 16 March 1840 with the first name Georges, and he was always known thereafter as Georges Bizet. His father Adolphe Armand Bizet (1810-86) was an amateur singer and composer, and his mother, Aimée Léopoldine Joséphine née Delsarte (1814-61), was the sister of the famous singing teacher François Delsarte.
He entered the Paris Conservatory of Music on 9 October 1848, a fortnight before his tenth birthday. His teachers there were Pierre Zimmermann (fugue and counterpoint; often assisted by his son-in-law Charles Gounod), Antoine François Marmontel (piano), François Benoist (organ) and, on Zimmermann's death, Fromental Halévy, whose daughter he himself later married. He won first prizes for organ and fugue in 1855 and completed his earliest compositions.
His first symphony, the Symphony in C, was written in November 1855, when he was seventeen, evidently as a student assignment. It was unknown to the world until 1933, when it was discovered in the archives of the Paris Conservatory library. Upon its first performance in 1935, it was immediately hailed as a junior masterwork and a welcome addition to the early Romantic period repertoire. The symphony bears a stylistic resemblance to the first symphony of Gounod, first played earlier in the same year, and which Bizet had arranged for two pianos although present-day listeners may discern a similarity to music of Franz Schubert, whose work was little known in France at the time the symphony was written.
In 1857, a setting of the one-act operetta Le docteur Miracle won him a share in a prize offered by Jacques Offenbach. He also won the music composition scholarship of the Prix de Rome, the conditions of which required him to study in Rome for three years. There, his talent developed as he wrote such works as the opera buffa Don Procopio (1858-59). There he also composed his only major sacred work, Te Deum (1858), which he submitted to the Prix Rodrigues competition, a contest for Prix de Rome winners only. Bizet failed to win the Prix Rodrigues, and the Te Deum score remained unpublished until 1971. He made two attempts to write another symphony in 1859, but destroyed the manuscripts in December of that year. Apart from this period in Rome, Bizet lived in the Paris area all his life.
Shortly after leaving Rome in July 1860, but while still touring in Italy, he had the idea of writing a symphony in which each of the four movements would be a musical evocation of a different Italian city – Rome, Venice, Florence and Naples. On hearing of his mother's serious illness he cut short his Italian travels and returned to Paris in September 1860; she died a year later. The Scherzo of the symphony was completed by November 1861, but it was not until 1866 that the first version of the whole symphony was written. He subjected it to a number of revisions through to 1871, but died before ever producing what he considered the definitive version. For this reason, the work is sometimes described as "unfinished", but this is an inaccurate description as it was fully scored. It was published in 1880 as the Roma Symphony.
Bizet was born at 26 rue de la Tour d'Auvergne in the 9th arrondissement of Paris in 1838. He was registered with the legal name Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, but he was baptised on 16 March 1840 with the first name Georges, and he was always known thereafter as Georges Bizet. His father Adolphe Armand Bizet (1810-86) was an amateur singer and composer, and his mother, Aimée Léopoldine Joséphine née Delsarte (1814-61), was the sister of the famous singing teacher François Delsarte.
He entered the Paris Conservatory of Music on 9 October 1848, a fortnight before his tenth birthday. His teachers there were Pierre Zimmermann (fugue and counterpoint; often assisted by his son-in-law Charles Gounod), Antoine François Marmontel (piano), François Benoist (organ) and, on Zimmermann's death, Fromental Halévy, whose daughter he himself later married. He won first prizes for organ and fugue in 1855 and completed his earliest compositions.
His first symphony, the Symphony in C, was written in November 1855, when he was seventeen, evidently as a student assignment. It was unknown to the world until 1933, when it was discovered in the archives of the Paris Conservatory library. Upon its first performance in 1935, it was immediately hailed as a junior masterwork and a welcome addition to the early Romantic period repertoire. The symphony bears a stylistic resemblance to the first symphony of Gounod, first played earlier in the same year, and which Bizet had arranged for two pianos although present-day listeners may discern a similarity to music of Franz Schubert, whose work was little known in France at the time the symphony was written.
In 1857, a setting of the one-act operetta Le docteur Miracle won him a share in a prize offered by Jacques Offenbach. He also won the music composition scholarship of the Prix de Rome, the conditions of which required him to study in Rome for three years. There, his talent developed as he wrote such works as the opera buffa Don Procopio (1858-59). There he also composed his only major sacred work, Te Deum (1858), which he submitted to the Prix Rodrigues competition, a contest for Prix de Rome winners only. Bizet failed to win the Prix Rodrigues, and the Te Deum score remained unpublished until 1971. He made two attempts to write another symphony in 1859, but destroyed the manuscripts in December of that year. Apart from this period in Rome, Bizet lived in the Paris area all his life.
Shortly after leaving Rome in July 1860, but while still touring in Italy, he had the idea of writing a symphony in which each of the four movements would be a musical evocation of a different Italian city – Rome, Venice, Florence and Naples. On hearing of his mother's serious illness he cut short his Italian travels and returned to Paris in September 1860; she died a year later. The Scherzo of the symphony was completed by November 1861, but it was not until 1866 that the first version of the whole symphony was written. He subjected it to a number of revisions through to 1871, but died before ever producing what he considered the definitive version. For this reason, the work is sometimes described as "unfinished", but this is an inaccurate description as it was fully scored. It was published in 1880 as the Roma Symphony.
Rossini

Gioachino Antonio Rossini (February 29, 1792 – November 13, 1868) was a popular Italian composer who created 39 operas as well as sacred music and chamber music. His best known works include Il barbiere di Siviglia (The Barber of Seville), La Cenerentola and Guillaume Tell (William Tell).
Rossini's most famous opera was produced on February 20, 1816 at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. The libretto by Cesare Sterbini, a version of Pierre Beaumarchais' infamous stage play Le Barbier de Séville, was the same as that already used by Giovanni Paisiello in his own Barbiere, an opera which had enjoyed European popularity for more than a quarter of a century. Much is made of how fast Rossini's opera was written, scholarship generally agreeing upon two weeks. Later in life, Rossini claimed to have written the opera in only twelve days. It was a colossal failure when it premiered as Almaviva; Paisiello’s admirers were extremely indignant, sabotaging the production by whistling and shouting during the entire first act. However, not long after the second performance, the opera became so successful that the fame of Paisiello's opera was transferred to Rossini's, to which the title The Barber of Seville passed as an inalienable heritage.
Rossini's most famous opera was produced on February 20, 1816 at the Teatro Argentina in Rome. The libretto by Cesare Sterbini, a version of Pierre Beaumarchais' infamous stage play Le Barbier de Séville, was the same as that already used by Giovanni Paisiello in his own Barbiere, an opera which had enjoyed European popularity for more than a quarter of a century. Much is made of how fast Rossini's opera was written, scholarship generally agreeing upon two weeks. Later in life, Rossini claimed to have written the opera in only twelve days. It was a colossal failure when it premiered as Almaviva; Paisiello’s admirers were extremely indignant, sabotaging the production by whistling and shouting during the entire first act. However, not long after the second performance, the opera became so successful that the fame of Paisiello's opera was transferred to Rossini's, to which the title The Barber of Seville passed as an inalienable heritage.
The Doors

The Doors were an American rock band formed in 1965 in Los Angeles by vocalist Jim Morrison, keyboardist Ray Manzarek, drummer John Densmore, and guitarist Robby Krieger. They were considered a controversial band, due mostly to Morrison's cryptic lyrics and unpredictable stage persona. The band dissolved in March 1973, short of two years after Morrison's death in July 1971. According to the RIAA, they have sold over 32 million albums in the US alone.
The Doors' music during the 1965-68 era was a fusion of hard rock, blues-rock, and acid rock. The origins of The Doors lay in a chance meeting between acquaintances and fellow UCLA film school alumni Jim Morrison and Ray Manzarek on Venice Beach California in July 1965. Morrison told Manzarek he had been writing songs (Morrison said "I was taking notes at a fantasic rock-n-roll concert going on in my head") and, at Manzarek's encouragement, sang "Moonlight Drive". Impressed by Morrison's lyrics, Manzarek suggested they form a band.
The Doors' music during the 1965-68 era was a fusion of hard rock, blues-rock, and acid rock. The origins of The Doors lay in a chance meeting between acquaintances and fellow UCLA film school alumni Jim Morrison and Ray Manzarek on Venice Beach California in July 1965. Morrison told Manzarek he had been writing songs (Morrison said "I was taking notes at a fantasic rock-n-roll concert going on in my head") and, at Manzarek's encouragement, sang "Moonlight Drive". Impressed by Morrison's lyrics, Manzarek suggested they form a band.
Henry Purcell

Henry Purcell (pronounced /ˈpɜrsəl/; 10 September 1659 (?) – 21 November 1695), was an English organist and Baroque composer of secular and sacred music. Although Purcell incorporated Italian and French stylistic elements into his compositions, his legacy was a uniquely English form of Baroque music.
Martin O'Donnell

Martin "Marty" O'Donnell (born May 1, 1955) is an award-winning American composer known for his work on video game developer Bungie's series, such as Myth, Oni, and most predominately Halo. O'Donnell collaborates with his musical colleague Michael Salvatori for many of the scores; he has also directed voice talent and sound design for the Halo trilogy, and is currently Bungie's Audio Lead.
O'Donnell began his music career writing television and radio jingles as well as scoring for radio and film. O'Donnell moved to composing video game music when his company, TotalAudio, did the sound design for the 1997 title Riven. After producing the music for Myth II, Bungie contracted O'Donnell to work on their other projects, including Oni and the code-named project that would become Halo: Combat Evolved. O'Donnell ended up joining the Bungie staff only ten days before the studio was bought by Microsoft, and has been the audio director for all Bungie projects since.
O'Donnell's score to the Halo trilogy has been called iconic, and the commercial soundtrack release of the music to Halo 2 became the best-selling video game soundtrack of all time. His most recently released work is the music for Halo: Reach, released digitally on September 14, 2010.
O'Donnell began his music career writing television and radio jingles as well as scoring for radio and film. O'Donnell moved to composing video game music when his company, TotalAudio, did the sound design for the 1997 title Riven. After producing the music for Myth II, Bungie contracted O'Donnell to work on their other projects, including Oni and the code-named project that would become Halo: Combat Evolved. O'Donnell ended up joining the Bungie staff only ten days before the studio was bought by Microsoft, and has been the audio director for all Bungie projects since.
O'Donnell's score to the Halo trilogy has been called iconic, and the commercial soundtrack release of the music to Halo 2 became the best-selling video game soundtrack of all time. His most recently released work is the music for Halo: Reach, released digitally on September 14, 2010.
Yuki Kajiura

Yuki Kajiura (梶浦 由記 Kajiura Yuki?, born August 6, 1965 in Tokyo, Japan) is a Japanese composer and music producer. She has provided the music for several popular anime series, such as the final Kimagure Orange Road movie, Noir, .hack//Sign, Aquarian Age, Madlax, My-HiME, My-Otome, .hack//Roots, Pandora Hearts, Puella Magi Madoka Magica, Sword Art Online, Tsubasa Chronicle and the Kara no Kyoukai movies (amongst others). She also assisted Toshihiko Sahashi with Mobile Suit Gundam SEED and Mobile Suit Gundam SEED Destiny. Kajiura has also composed for video games, including the cutscene music for Xenosaga II and the entire Xenosaga III game soundtrack.
Richard Rodgers

Richard Charles Rodgers (June 28, 1902 – December 30, 1979) was an American composer of music for more than 900 songs and for 43 Broadway musicals. He also composed music for films and television. He is best known for his songwriting partnerships with the lyricists Lorenz Hart and Oscar Hammerstein II. His compositions have had a significant impact on popular music down to the present day, and have an enduring broad appeal.
Rodgers is one of only two persons to have won an Oscar, a Grammy, an Emmy, a Tony Award, and a Pulitzer Prize (Marvin Hamlisch is the other).
Rodgers is one of only two persons to have won an Oscar, a Grammy, an Emmy, a Tony Award, and a Pulitzer Prize (Marvin Hamlisch is the other).
OneRepublic

OneRepublic is an American Rock band formed in Colorado. After a few years of moderate success, they have since drawn mainstream attention with the release of their single "Apologize," which has sold in excess of 7 million singles worldwide. The song, according to SoundScan Data, is one of only two songs that have reached 3 million legal downloads in history. A remix of "Apologize" was featured on Timbaland's Shock Value and the band's debut album, Dreaming Out Loud, produced by Greg Wells. Their debut album was released in the United States on November 20, 2007, with international release dates staggered throughout early 2008. As of June 14, 2008, Dreaming Out Loud had sold 761,298 copies in the U.S. with the bands total album sales coming to over 1.5 million worldwide so far. The band's second single, "Stop and Stare," has also crossed the 2 million mark in terms of worldwide single sales. Their third single, "Say (All I Need)", has been released in the UK and in the U.S. Their fourth single will be "Mercy", as stated by OneRepublic's MySpace page. The video has been streamed on Youtube.com.
Current members:
Ryan Tedder – Lead vocals, Guitar, Bass Guitar, Piano, Glockenspiel, Drums (2002–present)
Zach Filkins – Guitar, vocals (2002–present)
Drew Brown – Guitar, Bass Guitar, Glockenspiel (2002–present)
Eddie Fisher – Drums, percussion (2005–present)
Brent Kutzle – Bass guitar, keyboards, cello, vocals (2007–present)
Current members:
Ryan Tedder – Lead vocals, Guitar, Bass Guitar, Piano, Glockenspiel, Drums (2002–present)
Zach Filkins – Guitar, vocals (2002–present)
Drew Brown – Guitar, Bass Guitar, Glockenspiel (2002–present)
Eddie Fisher – Drums, percussion (2005–present)
Brent Kutzle – Bass guitar, keyboards, cello, vocals (2007–present)
Handel

George Frideric Handel (Friday, 23 February 1685 - Saturday, 14 April 1759) was a German-born Baroque composer who is famous for his operas, oratorios and concerti grossi. Born as Georg Friedrich Handel in Halle, he spent most of his adult life in England, becoming a subject of the British crown on 22 January 1727. His most famous works are Messiah, an oratorio set to texts from the King James Bible; Water Music; and Music for the Royal Fireworks. Strongly influenced by the techniques of the great composers of the Italian Baroque and the English composer Henry Purcell, his music was known to many significant composers who came after him, including Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven.
Handel's compositions include 42 operas; 29 oratorios; more than 120 cantatas, trios and duets; numerous arias; chamber music; a large number of ecumenical pieces; odes and serenatas; and sixteen organ concerti. His most famous work, the Messiah oratorio with its "Hallelujah" chorus, is among the most popular works in choral music and has become a centerpiece of the Christmas season. Also popular are the Opus 3 and 6 Concerti Grossi, as well as "The Cuckoo and the Nightingale", in which birds are heard calling during passages played in different keys representing the vocal ranges of two birds. Also notable are his sixteen keyboard suites, especially The Harmonious Blacksmith.
Handel introduced various previously uncommon musical instruments in his works: the viola d'amore and violetta marina (Orlando), the lute (Ode for St. Cecilia's Day), three trombones (Saul), clarinets or small high cornets (Tamerlano), theorbo, French horn (Water Music), lyrichord, double bassoon, viola da gamba, bell chimes, positive organ, and harp (Giulio Cesare, Alexander's Feast).
Handel's compositions include 42 operas; 29 oratorios; more than 120 cantatas, trios and duets; numerous arias; chamber music; a large number of ecumenical pieces; odes and serenatas; and sixteen organ concerti. His most famous work, the Messiah oratorio with its "Hallelujah" chorus, is among the most popular works in choral music and has become a centerpiece of the Christmas season. Also popular are the Opus 3 and 6 Concerti Grossi, as well as "The Cuckoo and the Nightingale", in which birds are heard calling during passages played in different keys representing the vocal ranges of two birds. Also notable are his sixteen keyboard suites, especially The Harmonious Blacksmith.
Handel introduced various previously uncommon musical instruments in his works: the viola d'amore and violetta marina (Orlando), the lute (Ode for St. Cecilia's Day), three trombones (Saul), clarinets or small high cornets (Tamerlano), theorbo, French horn (Water Music), lyrichord, double bassoon, viola da gamba, bell chimes, positive organ, and harp (Giulio Cesare, Alexander's Feast).
Borodin

Alexander Porfiryevich Borodin (12 November 1833 – 27 February 1887) was a Russian Romantic composer and chemist of Georgian–Russian parentage. He was a member of the group of composers called The Five (or "The Mighty Handful"), who were dedicated to producing a specifically Russian kind of art music. He is best known for his symphonies, his two string quartets, and his opera Prince Igor. Music from Prince Igor and his string quartets was later adapted for the musical Kismet.
Debussy

Achille-Claude Debussy (August 22, 1862 – March 25, 1918) was a French composer. Along with Maurice Ravel, he is considered one of the most prominent figures working within the field of Impressionist music, though he himself intensely disliked the term when applied to his compositions. Debussy was not only among the most important of all French composers but also was a central figure in all European music at the turn of the twentieth century.
Debussy's music virtually defines the transition from late-Romantic music to twentieth century modernist music. In French literary circles, the style of this period was known as Symbolism, a movement that directly inspired Debussy both as a composer and as an active cultural participant.
Debussy's music virtually defines the transition from late-Romantic music to twentieth century modernist music. In French literary circles, the style of this period was known as Symbolism, a movement that directly inspired Debussy both as a composer and as an active cultural participant.
Johann G. Albrechtsberger

Johann Georg Albrechtsberger (3 February 1736 – 7 March 1809) was an Austrian musician who was born at Klosterneuburg, near Vienna. Albrechtsberger died in Vienna; his grave is in St. Marx cemetery.
George Enescu

George Enescu, known in France as Georges Enesco, was a Romanian composer, violinist, pianist, conductor, and teacher. He is regarded by many as Romania's most important musician
Saint Saens
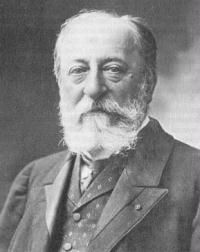
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (9 October 1835 – 16 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor, and pianist, known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse Macabre, Samson and Delilah, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo capriccioso, and his Symphony No. 3 (Organ Symphony).
Ruggero Leoncavallo

Ruggero Leoncavallo is an opera and operetta composer of the Italian modern era verismo.
 Sheet Music 365 is a site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
Sheet Music 365 is a site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.